Rotifers, Credit, BBC
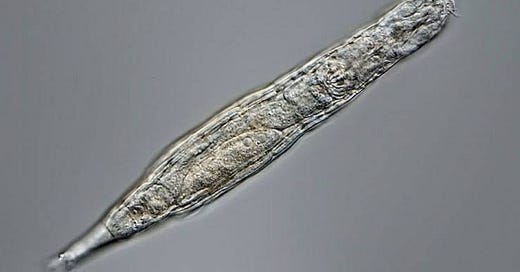
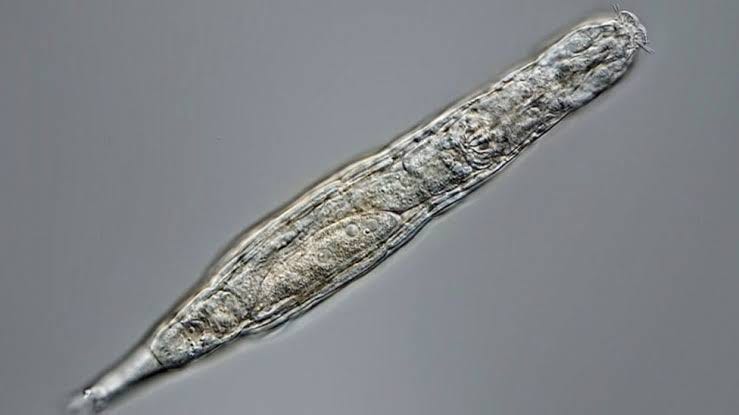
According to a new report, a type of zooplankton, rotifer, creates between 348,000 and 366,000 nanoplastics each day, with the creature responsible for the emergence of 13.3 quadrillion of plastic particles in Poyang Lake, the largest lake in China, no doubt because 23,000 individuals of the creature can exist in one liter of water at one location.
Five years ago, another report found that the Antarctic krill possesses the capacity to break down 31.5 micron polyethylene balls into particles less than one micron in diameter, with all the plastics leaving the creature's system in less than five days, giving small creature access to them as food.
In still another report, freshwater amphipods called gammarus duebeni fragment microplastics into nanoplastics 5,000 times smaller in size in just four days, making the spread of microplastics worse in Irish rivers, lakes and streams through the accelerated rate of break down.
The reports point to one fact. Animals such as zooplanktons, gammarus duebeni, and Antarctic krill own the ability to break down microplastics into even smaller particles, thereby play a huge role in the transport each year of an estimated 0.013 to 25 million metric tons of micro-and nanoplastics in up to thousands of kilometers by oceans, snow, sea spray or fog across nations, continents, and seas.
The total production of plastics ever made stands at an estimated 8.3 billion tons, but more than 50 percent finds the way to the ocean, where zooplanktons such as larvaceans can fragment them, as the creature can clear 11 gallons of seawater per hour, with their peak population possessing the capacity to clear the equivalent of 509 Olympic-sized swimming pool per hour.
According to a 2019 study, the amount of microplastics in the surface water near the Antarctic Peninsula stands at around 1,800 pieces per square kilometer, reaching about 900,000 in polluted areas like the Mediterranean Sea, meaning creatures like the Antarctic krill have access to the material as food.
Around 1,285 particles of microplastics exist per square foot of river sediments and 222,000 particles per square mile of Great Lakes waters and as much in Irish rivers and lakes, allowing amphipods such as gammarus duebeni to access them, splitting them into nanoplastics.
The worldwide prevalence of microplastics gives planktons and amphipods the opportunity to mistake the materials as food, and after breaking them down into nanoplastics, allow even smaller animals to consume them, increasing the amount of plastics in the animal population.
The oceans contain an estimated 38,000 gigatons of carbon and take up carbon from the atmosphere at the rate of about 2.7 gigaton annually. Planktons play a huge role in the storing of the carbon, but this could be disrupted through the presence of microplastics, because the presence of microplastics in marine creatures may clog carbon storage and slow the ocean's carbon uptake as well disrupt its nitrogen cycling.
After the sampling of 38 lakes and reservoirs around the world, including those in Australia, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe, researchers found plastics and microplastics in great quantities, but this could prove dangerous in the near future, as lakes provide a major route for microplastics discharge through the release of the materials into the sea, causing danger to amphipods and others.
The Southern Ocean absorbs about 550 million tons of carbon from the atmosphere each year, or about 18 percent of the amount absorbed by all of the world's oceans, but due to the transfer of microplastics to larger predators such as whales, penguins, and others, the oceans could be affected as one of the planet's largest carbon sinks.
The ingestion and breaking down of microplastics increase the amount of the material in the animal population as well as the oceans, but this could affect the water body as one of the planet's carbon sinks, reducing the capacity for ocean storage and accelerating the pace of climate change with faster carbon dioxide emissions.
For climate change to be managed, the worldwide prevalence of microplastics should be curtailed, so creatures don't have to break down the material into smaller bits, enhancing the transport of millions of plastic particles, which poses a danger to humans.
Four Exploding Products in Climate Tech
Power Electronics, Credit, Zephyr Project
As climate change intensifies with the use of fossil fuels, new technologies emerge to lessen the effects. Here are some of the exploding products with the new trend this week, important in the manufacture of solar panels. The trend here will provide ideas for activists, investors, creators, and founders.
(1) Diodes
The global power diodes market is driven by the increasing demand for efficient and reliable power electronics in various industries.
Power diodes are used for rectification, voltage regulation, and power conversion in applications such as industrial automation, consumer electronics, automotive, and renewable energy.
The global diode market size was evaluated at USD 7.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit around USD 10.5 billion by 2032 with a registered compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.85% over the forecast period 2023 to 2032.
(2) Thyristor
They halt power supply disruptions by connecting a Zener diode at the thyristor gate. When power supply voltage levels exceed the Zener voltage, the thyristor turns off the power supply output and activates circuit breakers or fuses upstream from the power supply.
The global thyristors devices market was valued at US$ 711.01 million in 2022 and is anticipated to reach US$ 1,064.86 million by 2029, witnessing a CAGR of 7.82% during the forecast period 2023-2029.
(3) Transistors
Power transistors amplify and switch the electrical signal in the power suppliers and power amplifiers. They are suitable when appliances use a large amount of current and voltage.
The global power transistor market size was valued at USD 13.56 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow from USD 13.76 billion in 2023 to USD 26.83 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 10.0% during the forecast period.
(4) Capacitors
Capacitors are electronic components that store electrical energy in an electric field. They consist of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the plates, an electric field is established, causing positive and negative charges to accumulate on the respective plates.
The global capacitor market size was evaluated at USD 34.65 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit around USD 61.83 billion by 2032 with a noteworthy CAGR of 5.96% from 2023 to 2032.
What to Eat
Nigerian vegan dish, Credit, Foodaciously





There are mounting possible unforeseen side-effects from our modern lifestyles; ingesting nanoplastics, exposure to 5G and unwise use of AI are just a few examples. If we inspire a global birth-strike we can begin to minimise exposure to these threats, as well as all the other escalating threats that we are observing. The UN Charter for Ecological Justice offers a vehicle to deliver the awareness required to inspire a global birth strike.
This is a most disturbing, quantitative, helpful article - thank you so much Ade. Plastics have been among the most significant metric of the Anthropocene, and wreaking havoc on everyone's health, including humans. Thank you for writing and sharing it. And yes, the food looks delicious, even for those who grew up in Nigeria and remember okra as 'slimy' (like my husband)!