Shrinking Population of Animals can only put Humans in Trouble
As animals now vanish 35 times faster than average
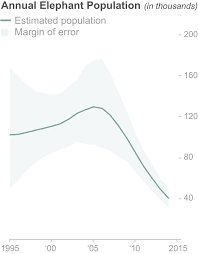
Shrinking population of elephants, Credit, National Geographic
Ten million African elephants roamed the continent at the beginning of the 20th century, but only about four hundred and fifty thousand of elephants now prowl the savanna, with all elephant population in some countries having gone extinct, the surviving ones scattered and declining.
At the onset of the 20th century, perhaps a million lions roamed throughout the Africa continent, but by the 1940s, only about 450,000 of them still existed, the number plunging to around 20,000 today, with the number continuing to drop, a 50 percent chance emerging that the lion population will be halved in the next two decades.
A total of about 2.9 million whales faced death through human activities between 1900 and 1999, so that for example now, about 5,000 of blue whales remain from a population of 340,000, a reduction of 98.5 percent while the fin whale suffered a decline of 45 percent of its numbers.
Apart from elephants, lions, and whales, many other animals show a drastic decline in population since the start of the 20th century, and it's not surprising that researchers find groups of animal species vanishing at a rate 35 times higher than the average, disappearing at a speed it would have taken them 18,000 years to happen.
Each year, at least 20,000 African elephants get poached for their tusks, leading to the shrinking of its population by 98 percent since the 16th century, from a population of 25 million to around 10 million to 1900 and down to 1.3 million by 1979 and now to 450,000 in the wild today.
Across Africa, lions now occupy less than eight percent of the land they once occupied, with the situation acute in the west and central regions of Africa, with a 90 percent decline in their connected habitats to before 1970, and the eastern and southern Africa experiencing 44 and 55 percent decline respectively in connected habitats.
Each year, an estimated minimum of 300,000 whales and dolphins get slaughtered as a result of fisheries bycatch, while other whales fall prey to challenges from habitat loss.
Therefore, human activity through habitat loss, illegal poaching, and overfishing forms the reasons behind the drastic decline in the population of lots of animal species since the start of the 20th century, but this presents a great danger to civilisation as a whole if biodiversity loss can't be controlled or eliminated.
Elephants play a role in carbon storage, because they increase it in a huge way, their decline leading to a dramatic fall in carbon capture, and some experts feel if the population of African forest elephants returned to its former size, it would increase carbon capture by 13 metric tons per hectare, equal to more than 6,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide per square kilometer, the same amount of carbon dioxide captured by over a quarter of a million trees.
Since a single lion kills about 15 larger animals each year, it acts as a top predator in the environment, keeping a healthy balance in the population of herbivores like zebras and buffalos, affecting the condition in relations to grasslands and forests.
Whales store carbon in their bodies while alive, but when they die, they sink to the bottom of the sea, sequestering 33 tons of carbon dioxide, taking a huge amount of the gas out of the atmosphere for centuries, with whale falls currently leading to the sequestration of 62,000 tons of carbon dioxide per year - equivalent to around 2.8 million trees, from 360,000 tons for the pre-whaling population.
By playing a huge role in carbon storage in the oceans, as well as keeping a healthy balance in the forests, animal species generally help to mitigate the effects of the climate change crisis currently bedeviling the planet, meaning a decline in their number through human activities worsens the situation on earth.
To reduce consequences of biodiversity loss, nations need to buy fewer products that fuel biodiversity loss. They need to reduce waste in consumer goods made from animals. They ought to invest in ways to protect biodiversity. Through this, the effects of climate change could be slowed down.
What to Eat
Kenyan vegan diet, Credit, The Veganary